Catfish and skipjack are two popular fish species that are often used as bait for fishing. While both fish are commonly used for bait, they have distinct differences that make them unique. Understanding these differences can help anglers choose the right bait for their fishing needs.
Catfish are a type of bottom-dwelling fish that are found in freshwater environments. They are known for their barbels, which are sensory organs that help them find food in the murky waters they inhabit. Catfish are also known for their sharp spines, which can be dangerous if not handled properly. They are a popular game fish and are often sought after by anglers for their size and fighting ability.
Skipjack, on the other hand, are a type of saltwater fish that are commonly found in the Atlantic Ocean. They are known for their oily flesh and are often used as bait for larger game fish such as tuna and marlin. Skipjack are also popular among anglers themselves, as they are a fast-swimming fish that can provide a fun challenge to catch. While they are not as well-known as catfish, they are still an important part of the fishing world.

Identification and Physical Characteristics
When it comes to identifying the difference between catfish and skipjack, there are several physical characteristics to consider. In this section, we will explore the features that set these two fish apart.
Skipjack Features
Skipjack herring, also known as Alosa chrysochloris, are a North American migratory fish species found in fresh and brackish waters. These fish are known for their golden-green, silvery coloration and gray to dark blue backs with dark streaks. One of the most distinguishing features of skipjack is their protruding lower jaw and teeth on their tongue and upper and lower jaw. They also have an oblong body with an eye diameter that is less than the snout length.
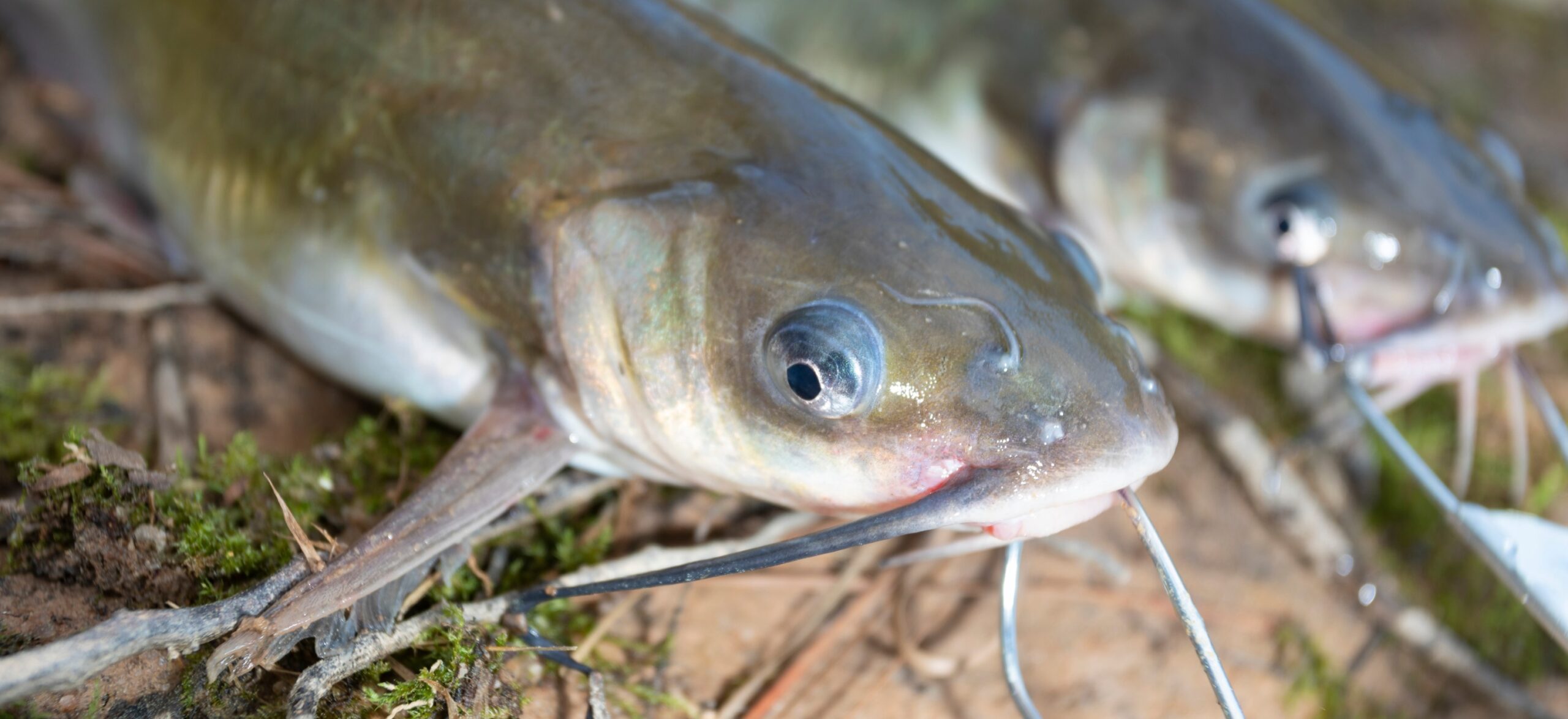
Catfish Features
Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish with over 3,000 species worldwide. These fish are named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat’s whiskers. Catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to smaller species that are commonly kept as pets.
One of the key features that distinguishes catfish from other fish species is their protruding lower jaw. They also have an adipose fin, which is a small fin located on their back behind the dorsal fin. Catfish come in a variety of colors, including brown, gray, and even black. Some species, like the blue catfish, have a forked tail and can be very similar to channel catfish. However, only the Rio Grande population of blue catfish has dark spots on the back and sides.
In terms of size, catfish can range from just a few inches to several feet long. The average size of a catfish varies depending on the species, but most are between 12 and 24 inches long.
Habitat and Distribution
Skipjack Habitat
Skipjack, also known as Atlantic bonito, are a type of tuna that inhabit warm waters of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. They prefer to live in open waters and are commonly found in the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, and along the eastern coast of the United States. Skipjack are primarily saltwater fish, but they can also tolerate brackish water.
Catfish Habitat
Catfish are a freshwater fish that can be found in rivers, lakes, and ponds throughout North America. They are commonly found in the eastern United States, particularly in the Ohio River and its tributaries. Catfish prefer slow-moving or still water and are often found near the bottom of rivers and lakes.
Catfish are also adaptable to different environments and can survive in a variety of water conditions. They can tolerate low oxygen levels and high levels of pollutants, making them a hardy species.
In summary, skipjack and catfish have different habitat preferences. Skipjack are primarily saltwater fish that inhabit the open waters of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, while catfish are freshwater fish that can be found in rivers, lakes, and ponds throughout North America.
Diet and Predatory Behavior
Skipjack Diet
Skipjack tuna primarily feed on small fish such as shad, herring, and minnows. They are known to feed on a variety of bait, including live bait and cut bait. Anglers often use skipjack as bait for larger fish, including catfish.
Catfish Diet
Catfish have a diverse diet that includes both natural prey and other food sources. They are known to feed on a variety of baits, including worms, shrimp, and small minnows. Understanding the diet of catfish is essential in comprehending their feeding habits and behavior. Catfish are opportunistic feeders and will eat a variety of prey, including other fish. In fact, some catfish species, such as the blue catfish, primarily feed on fish earlier in life.
In summary, skipjack tuna primarily feed on small fish, while catfish have a more diverse diet that includes natural prey and other food sources. Both skipjack and catfish are known to feed on a variety of baits, including live bait, cut bait, and worms.
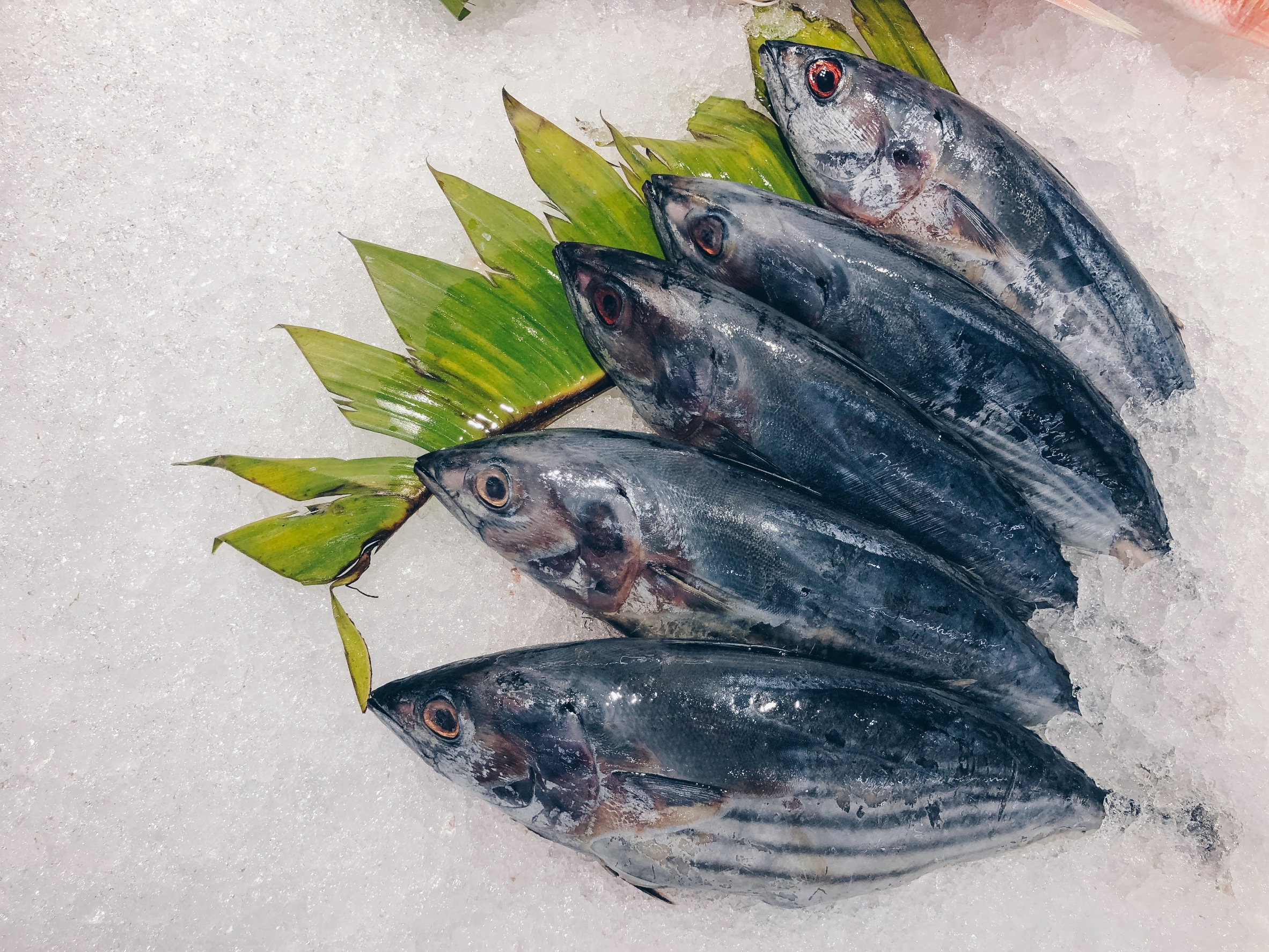

Fishing Techniques and Bait
Skipjack Fishing Techniques
Skipjack are a popular baitfish for catfish anglers. They can be caught using sabiki rigs, cast nets, or by trolling. Anglers can use a variety of lures to catch skipjacks, including small jigs, spinners, and spoons. Once caught, skipjack can be used as fresh bait or frozen for later use. To use skipjack as bait, anglers can cut them into chunks or fillets and use treble hooks to secure them.
Drift fishing is an effective technique for using skipjack as bait. Anglers can drift along the current, allowing the bait to move naturally in the water. This technique can be used to catch blue catfish, channel catfish, and flatheads.
Catfish Fishing Techniques
When fishing for catfish, anglers can use a variety of techniques and baits. Channel catfish are often caught using punch bait, which is a sticky mixture of ingredients like cheese, garlic, and catfish feed. This bait is typically used with a treble hook and fished on the bottom.
Flathead catfish prefer live bait, such as gizzard shad or carp. These baits can be caught using a cast net or purchased from a bait shop. Anglers can use a slip sinker rig to present the bait near the bottom of the water column.
Blue catfish can be caught using fresh bait, such as cut skipjack or fresh chicken livers. Anglers can also use frozen bait, like canned tuna or hot dog slices. Garlic and crawfish scents can be added to the bait to attract fish.
Overall, successful catfishing requires fresh bait, a variety of techniques, and patience. Anglers should experiment with different baits and techniques to find what works best for them.
Species and Varieties
Skipjack Species
Skipjack tuna, also known as Katsuwonus pelamis, are a species of tuna that are commonly found in tropical and subtropical waters around the world. They are the smallest and most abundant of the major commercial tuna species, with a streamlined body that is mostly without scales. Their backs are dark purple-blue, and their lower sides and bellies are silver with four to six dark bands.
Skipjack herring, also known as Alosa chrysochloris, are a type of herring that are found in freshwater rivers and lakes in North America. They are known for their silver scales and greenish-blue backs.
Skipjack shad, also known as Alosa chrysochloris, are a type of herring that are found in freshwater rivers and lakes in North America. They are known for their silver scales and greenish-blue backs.
Catfish Species
Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish that are found in freshwater and saltwater habitats around the world. They are named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat’s whiskers. Some of the most common species of catfish include:
-
- Blue catfish, also known as Ictalurus furcatus, are a species of catfish that are found in freshwater rivers and lakes in North America. They are known for their blue-gray color and their ability to grow to large sizes.
Overall, the main difference between skipjack and catfish species is their habitat and physical characteristics. While skipjack tuna are primarily found in saltwater habitats and have a streamlined body without scales, catfish are found in freshwater and saltwater habitats and have prominent barbels. Additionally, skipjack tuna are typically consumed as a food source, while catfish are often caught for sport fishing.
Conservation and Abundance
Skipjack tuna is the most abundant and smallest of the major commercial tuna species, according to WWF. They are found in oceans and can live up to eight to ten years. Currently, skipjack tuna is not considered endangered by the IUCN. However, overfishing is still a concern, and it is important to manage skipjack tuna populations to ensure their sustainability. The WWF recommends that consumers choose skipjack tuna caught using pole and line or handline methods, which have less impact on other marine life.
In contrast, catfish populations vary depending on the species and location. Some species, such as the blue catfish, have become invasive in some areas and have negatively impacted native fish populations. However, other species, such as the flathead catfish, are considered threatened in some states due to habitat loss and overfishing. The IUCN does not have a conservation status for all catfish species, but some are listed as vulnerable or endangered. It is important to follow local regulations and guidelines when fishing for catfish to help manage their populations and protect their habitats.
Overall, it is crucial to consider the conservation and abundance of both skipjack and catfish when fishing. By choosing sustainable fishing methods and following regulations, anglers can help ensure the long-term survival of these important species.
Culinary Uses and Taste
Both catfish and skipjack tuna are popular fish for consumption. Catfish meat is known for its mild and sweet flavor, while skipjack tuna has a stronger flavor profile. Catfish meat is also known for its tender and flaky texture, while skipjack tuna has a firmer texture.
Catfish is a versatile fish that can be cooked in a variety of ways, such as frying, grilling, or baking. It is commonly used in Southern cuisine, particularly in dishes like catfish po’ boys and catfish gumbo. Skipjack tuna, on the other hand, is commonly used in canned tuna and is often sold as “chunk light” tuna.
In terms of nutritional value, skipjack tuna is a leaner fish with less fat than catfish. However, catfish is a good source of protein and contains vitamins and minerals such as vitamin B12 and selenium. Skipjack tuna is also a good source of protein and contains vitamins and minerals such as vitamin B3, vitamin B6, and magnesium.
When it comes to other types of fish, catfish is often compared to mahi mahi, which also has a mild flavor and tender texture. Skipjack tuna is often compared to other types of tuna, such as albacore and false tuna, which have their own distinctive qualities in terms of texture and taste.