Catfish is a very popular fish found in many places around the world. There are many species of catfish. Red drum is also a popular game fish that has many uses. These two fish are very different, but what are their differences?
First of all, catfish is a species of fish that contains several different fish, but the red drum is just one species of fish. That there are more differences between them, such as the fact that both of these fish look entirely different.
To start, catfish are from Siluriformes, while the red drum is from Acanthuriformes.
Similarly, there are other differences between them. Keep reading to learn all the different ways that catfish and red drums are unique from each other.
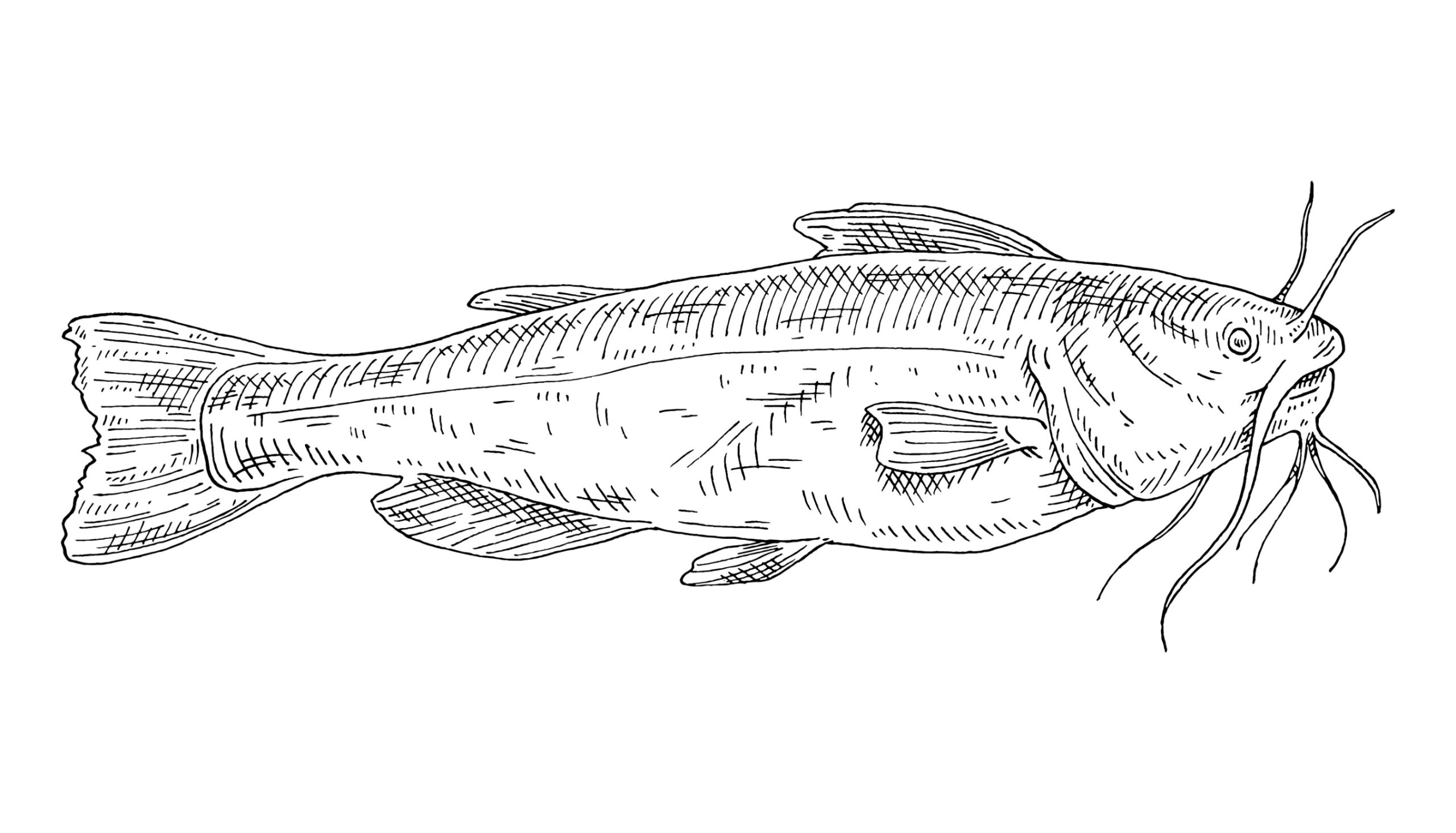
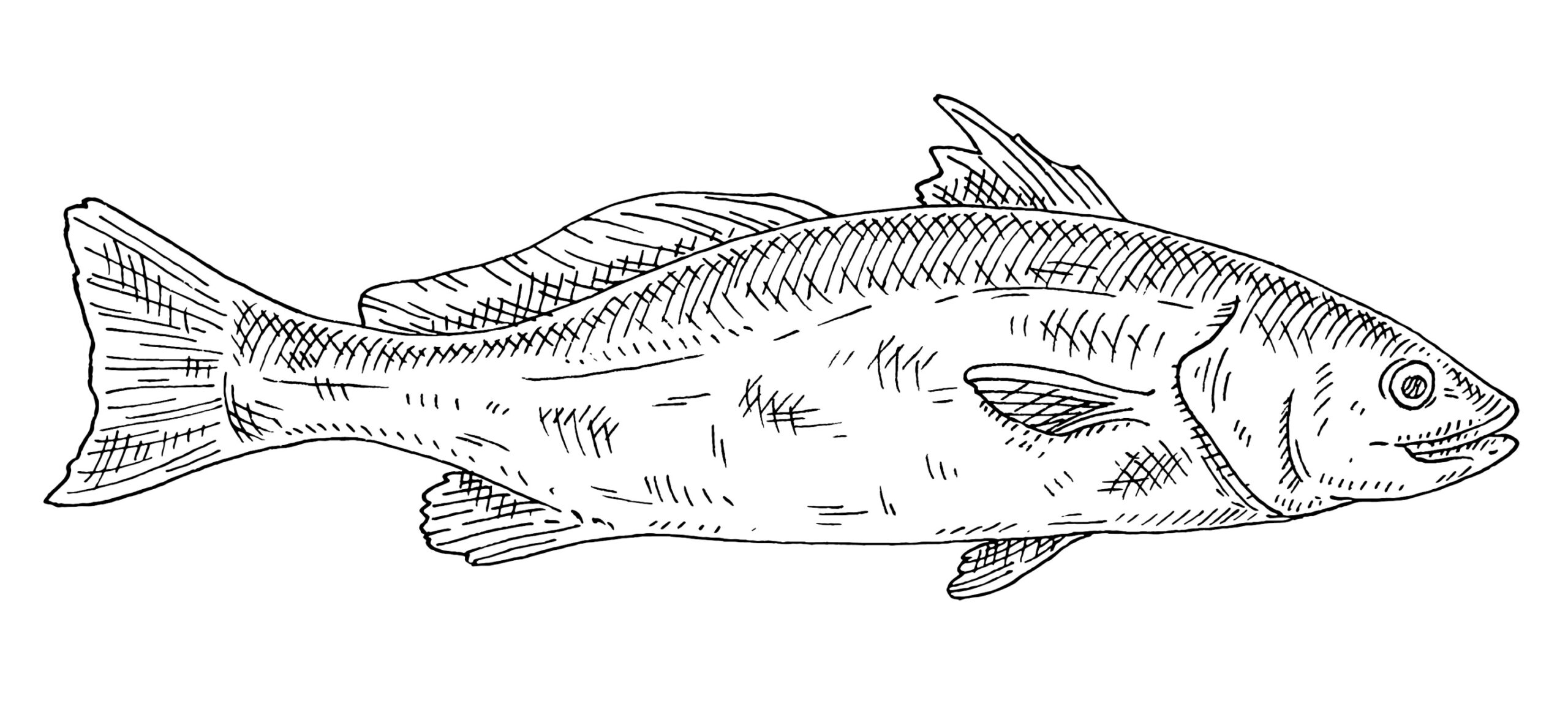
The appearance
The first significant difference between the two is in appearance. No one will ever confuse the two fish because they look so distinct.
The catfish is a fish with no scales; it is one of the few fish with no scales. Instead, the catfish’s body is very smooth and slimy, so it can slip between rocks and eat from the bottom of the water. However, the catfish does have sharp fins that can penetrate the prey. Moreover, the catfish has barbels, whiskers on the side of its mouth, and a chin that helps it navigate its muddy environment. Despite these significant differences, the catfish has a cylindrical body with a flattened ventrum to allow benthic feeding at the bottom. Most catfish do not have teeth and either suck the prey in or swallow it whole. When it comes to color, it depends on the species, but usually, they are darker in color, like grey, brown, or black, with a white belly to blend in with their habitat.
Juvenile and adult catfish are very similar. The juvenile has a large head and eyes, which might become more balanced as it matures, but overall, they are similar. Even the coloration of the juvenile catfish might follow that of the adult catfish.
Now, when it comes to the red drum fish, it looks pretty different. Overall, the red drum fish does not have barbels or whiskers; it also has proper scales and fins like most fish do. Also, red drum fish have a streamlined body with large scales and a pointed head. One distinct feature of the red drum fish is its one large black spot on the upper part of the tail base, sometimes even two. This is so that the predator attacks their tail instead of their head.
When the fish is juvenile, it has many more black spots, but they disappear as they age. As you can tell by their name, the fish is dark red on the back, which fades to black. Also, true to its name, the fish makes knocking or drumming sounds during spawning by vibrating their swim bladders.
The size and lifespan
The size of the catfish varies and depends on the type of fish and where it is located. Overall, the size and lifespan of fish depend a lot on their diet, habitat, and other environmental factors, like if there are a lot of predators in the water.
Catfish are fish with a lot of variation in size, but most of them grow to be almost five inches long, but some catfish are as small as 0.4 inches in length. However, there are many more prominent species. Specifically, a blue catfish was caught and weighed 143 pounds, and it was 57 inches long. Therefore, the catfish can get more considerable than the assumed size. Also, there are many larger-sized species of catfish.
The lifespan of catfish again depends on the species. For example, channel catfish, a common species in North America, can live for up to 20 to 25 years in the wild. The blue catfish, another popular species, can live for 30 to 40 years. Other catfish species, such as the Mekong giant catfish, can live for up to 60 years or more.
When it comes to the red drum, since it is only one species of fish, it has a more distinct size. The fish can grow to be between 18 and 27 inches in length and weigh between 5 and 10 pounds. Like catfish, the largest red drum caught was 94 pounds, so much bigger than the assumed size of the fish.
Red drums’ lifespan is much shorter than most catfish species. The average lifespan of red drum fish in the wild is around eight to 10 years, although some individuals can live up to 30 years. It depends on how much prey there is in the water and if the fish has a lot of predators in the water or not. Most fish do not die of natural causes, so it is impossible to find their exact lifespan.
The habitat
The habitats of both catfish and red drum are different too. Catfish are in all coastal waters of every continent except Antarctica.
These fish are the most common in South America, Africa, and Asia, with some families in Europe and North America. Most are located in freshwater environments. They are found in shallow water, where they inhibit the bottom, muddy substrates. However, catfish can be found in lakes, rivers, streams, ponds, and even underground water systems, depending on the species. Also, since the fish do not have excellent hunting skills, they tend to favor areas with abundant covers, such as rocks, logs, and vegetation, which protect them from predators and shade from the sun.
Some catfish can live in very low-oxygenated areas because they are adapted to respire from the skin. Catfish are also known to migrate for food and suitable breeding grounds. Some species, like blue catfish, undergo long-distance migrations from their wintering grounds to spawning environments.
The red drum is a fish that has a more distinct habitat. These fish are found on the eastern and southern Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts of Louisiana, Alabama, Mississippi, Texas, Florida, Georgia, the Carolinas, and Virginia. Recently, red drum were also found in the Mediterranean Sea. These fish swim in soft, sandy, or muddy bottom areas, often congregating around submerged structures such as oyster reefs, rocks, and shipwrecks. Water temperature is an essential factor, as these fish prefer warmer waters.
Juvenile red drum fish stay in estuaries, bays, and tidal creeks, where they can find protection from predators and access various food sources. As they mature, they move into deeper waters along the coast, including inlets, jetties, and nearshore reefs. Adult red drum fish may also migrate into deeper offshore waters during winter. This is because the fish only prefer water temperatures between 68 and 86 degrees Fahrenheit and are more active around 72- and 78-degrees Fahrenheit.
The diet
The diet of catfish is very opportunistic, but they could be better hunters, so they forge for food at the bottom of the water in muddy areas. This is why most catfish are omnivorous and eat both plants and animals.
When necessary, the fish feed on insects, crustaceans, mollusks, fish, and even plant materials. Young catfish typically feed on small aquatic invertebrates such as insect larvae and crustaceans. As they grow, they may feed on larger prey, such as fish and mollusks. The catfish has a remarkable ability to smell and forge food and will also eat dead or decaying organic matter.
The diet of red drum consists of crabs, shrimp, and mullet, in the spring and winter, adults primarily feed on menhaden, mullet, pinfish, sea robin, lizardfish, spot, Atlantic croaker, and mud minnows. They are also bottom feeders, usually found in the middle of the water column. Juvenile red drum fish feed on small invertebrates such as shrimp, crabs, and worms. They may feed on larger prey such as fish, squid, and other crustaceans as they grow. Adult red drum fish may also consume larger fish, such as menhaden and mullet. These fish are good hunters, unlike catfish.
The reproduction method
The reproduction method is straightforward for both fishes. However, some catfish can change their sex as they grow older. Since there are so many species of catfish, not all of them reproduce in the same way.
The fish reproduce when the female catfish releases eggs, and the male catfish releases sperm to fertilize the eggs. Of course, before that, the male catfish needs to court the female catfish to be ready to release the eggs. Once the eggs are fertilized, they are usually kept safe by the male fish. Some male fish build a nest, but other times, they can lay the fertilized eggs in crevices and rocks until they hatch. Usually, the male fish guards the eggs until they hatch, but sometimes, like in the case of blue catfish, the eggs are allowed to drift away.
The red drum has similar reproduction habits to catfish, but they only reproduce in late summer and early autumn. Females release eggs into the water column, and males release sperm to fertilize the eggs, like catfish. However, the male red drum does not guard the eggs in this case. The fertilized eggs hatch into larvae, which are carried by ocean currents and eventually settle into coastal estuaries. The place where they reproduce varies from habitat to habitat.
The nutritional composition
Both catfish and red drum are fish that are eaten and have a specific nutritional composition, making them healthy.
The catfish has a lot of protein. It has 16–20 grams of protein for a 100-gram fillet. Similarly, a 100-gram fillet of catfish also has 4 to 6 grams of fat and, in total, 90 to 120 calories. The catfish is also very rich in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins and minerals such as vitamin B12, vitamin D, selenium, phosphorus, and potassium.
The red drum is also a fish that is eaten a lot. A 100-gram fillet of red drum contains the same amount of protein as a catfish fillet but less fat, as it has 1 gram to 5 grams of fat. The calories in the red drum are higher compared to catfish. However, it is still a relatively low-calorie fish, with 100 to 150 calories per 100-gram fillet. Red drum also has a lot of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B12, vitamin D, selenium, phosphorus, and potassium, like catfish.
The taste
The taste of catfish depends on the species and where it was caught. A farm-raised catfish generally tastes much cleaner and sweeter than the one you catch because the diet of the fish can be controlled in captivity.
The catfish has a sweet and mild taste, and it can be cooked in many ways, including grilled, baked, fried, and sautéed. It is often seasoned with spices, herbs, or a flavorful marinade to enhance its flavor. Catfish skin is considered inedible because it is too tough, but many people still eat it. However, it would help to be careful since catfish is a bottom-dwelling fish; its diet is not the cleanest and can taste muddy.
The red drum is a slightly sweet fish that has a firm flake. The taste is very different from that of catfish, as red drum is known to have a clean taste. Like catfish, the red drum is a versatile fish that can be prepared in various ways, including grilled, blackened, baked, fried, or sautéed. Eating a red drum that is younger is recommended, as it has a better flavor. It pairs well with various flavors and ingredients, including citrus, herbs, spices, and vegetables. The skin of the red drum is edible as well, and many people enjoy its skin.
Conclusion
Both catfish and red drum are popular fish eaten and caught by many people. These game fish have many purposes, and it is hard to confuse the two.











