In the family Malapteruridae, the genera Malapterurus and Paradoxoglanis contain a total of 18 species of freshwater catfish found throughout tropical Africa. To protect itself and catch prey, the catfish can release a shock of up to 450 volts. The jolt also aids in their exploration of the surrounding area. There is no evidence that this release is fatal to humans, but it can be painful. Some people even keep electric catfish in aquariums as pets.
Power is its primary means of self-defence and hunting. The electric organ, made of modified muscle tissue, is a thin, gelatinous layer below the fish’s delicate, bare skin. Various depictions of it were found on Egyptian tomb walls. Because of its resilience and aggressive nature, you can keep electric catfish in private aquariums.
A Look at the Fascinating Facts on Electric Catfish
-
- You can find Artwork of electric catfish in ancient Egyptian tombs. After receiving an electric shock from this fish, the fishermen would throw back their entire catch, saving many fish from being eaten.
-
- Most electric catfish will not share territory with another. They may use electric shocks as the first line of defense against intruders of a different species. Defenders typically show an open mouth and sway back and forth in an arched position. It will start biting and shocking the intruder if that doesn’t work.
-
- Many species of electric catfish are strictly nocturnal. The first four or five hours after sundown are peak activity times for them. They spend the rest of the day cowering under its protection.
Features and Appearance of Electric Catfish
Electric catfish can serve five different purposes: (1) predation and feeding; (2) defense, attack, and protection; (3) defense, chase, and exploration; (4) prey detection; and (5) intraspecific assessment.
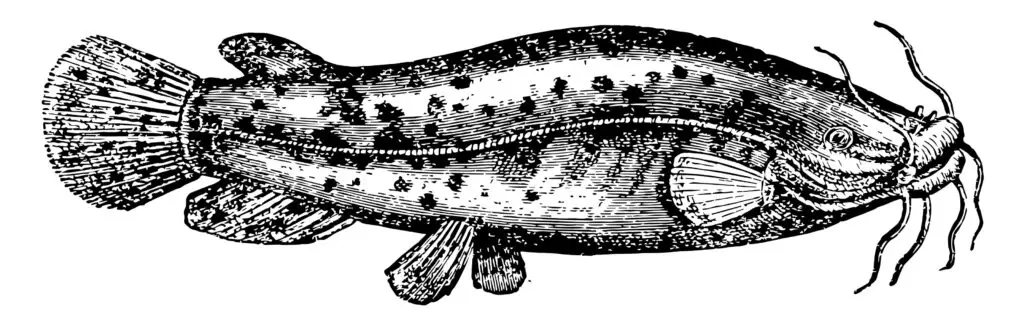
In full maturity, members of this family can reach lengths of up to 4 feet from snout to tail, though the majority are typically between 2 and 3 feet in length. The common color of their backs and sides is grey-brown. Around the belly button, this gradually transitions to a white or cream color.
The electric catfish doesn’t stand out much compared to other fish in its family. Thick lips, tiny eyes, a rounded snout, and three sets of barbels distinguish its long, stout body, sensing organs that resemble whiskers. The dorsal, back, fin is completely absent from this fish, which instead has rounded pectoral and pelvic fins.
In addition, some individuals have irregular black spots all over their sides. During the day, electric catfish spend their time hiding from predators. The peak hunting and feeding times for M. electricus occur four to five hours after sunset.
Electric Catfish Behavior
Defending their territory from potential threats is a top priority for territorial electric catfish, so they will use their electrical ability aggressively. Open-mouth displays are the first sign of aggression in fish when another member of their species confronts them. Lateral displays follow. The fish stand “antiparallel,” swaying back and forth with arched bodies, pushing and rubbing against each other in lateral displays. They change how they expel waste when a species member enters their territory.
In tense situations, individuals may resort to more aggressive behavior, such as barbel, flank bites, or lateral displays. In a barbell grip, one or both fish hold on to the other’s barbels for about 15 to 20 seconds while flailing around. In a flank bite, one fish quickly spins its head around and bites the flanks of the other, holding on for several minutes. Usually, these short performances last no more than 15 seconds and wrap up a meeting.
Reproduction and Longevity of Electric Catfish
The catfish’s reproductive habits are largely known, and if it’s anything like other members of the catfish order, it won’t start spawning until the water temperature is just right. During mating season, the fish will construct a nest along the clay shores of a river or lake, measuring about 10 feet in length. The female fish’s size and age determine the nest’s egg count.
Spawning occurs when the male’s sperm is introduced. To what extent the male will protect the nest from predators is unknown. In most cases, the fry will leave the nest a short while after hatching and must learn to survive on its own until they reach maturity. A rough estimate puts the average lifespan in the wild at around 10 years.
Distribution, Population, and Habitat of Electric Catfish
The electric catfish inhabit the rivers and lakes of Africa’s continent, especially the mighty Nile. They thrive in muddy, secluded bodies of water where they can easily conceal themselves. Each species has a unique population status. Even though the majority of species are classified as “least concern” on the IUCN Red List, a few are “data deficient,” which means that scientists simply don’t know enough about the size of their populations. In the wild, they don’t seem to have many enemies. In its native environment, the electric catfish is a top predator. Those long barbels of theirs are perfect for digging in the soil.
Consumption and Taste of Electric Catfish
In some regions of Africa, Electric Catfish are prepared and consumed as food. In the region surrounding Lake Kainji, smoked electric catfish is a very well-liked delicacy. The stomach of a wild-caught catfish has a flavor that is described as muddy and dirty. Once cooked, Electric Catfish has a flavor that is slightly sweet and mild, with a dense and moist texture, and it flakes less than other white fish. The fish takes on the flavor of the seasonings and is typically coated in cornmeal, you can enjoy all the flavors working together.
How to Catch an Electric Catfish
Catfish are relatively easy to fish for but while hunting an electric catfish, you should wear protective clothing, such as thick rubber gloves. However, it is not guaranteed that you won’t get an electric shock while holding an electric catfish.
What sort of food does the electric catfish prefer?
The electric catfish paralysis its prey with an electric discharge and then consumes them or their eggs. It’s safe to assume that these creatures are opportunistic feeders, either waiting for prey to wander into their territory accidentally or patiently sifting through the soil to find something edible.
Conclusion
These fish are popular in home aquariums because they provide a lot of entertainment value and a food source for other fish. They come in various colors and patterns, making them an interesting addition to any tank. If you’re interested in getting an electric catfish for your home aquarium, check out the different types available on the market today.











