The Rock Hind Grouper, also known as Epinephelus adscensionis, is a marine fish species belonging to the Serranidae family of groupers. It is a carnivorous fish typically found on rocky reefs and ledges in the Western Atlantic Ocean, ranging from North Carolina to Brazil, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.
The Rock Hind Grouper is a medium- to large-sized fish. It has a mottled coloration with shades of brown, orange, and red and a distinct black spot on its tail. It is a popular game fish often sought after by anglers for its firm, white flesh. However, due to overfishing, it is now considered a species of concern and is subject to fishing regulations in some areas.
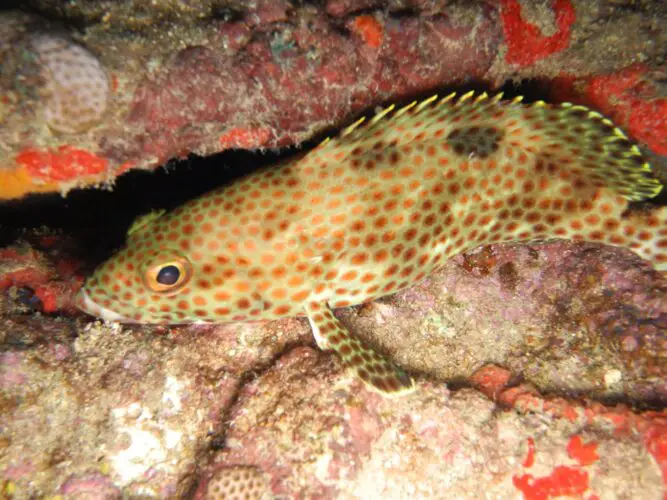

Appearance and Physical Characteristics
A fish of average size, the Rock Hind Grouper can reach lengths of 24 inches and weighs 14 pounds. It has an olive-brown body that is strong and elongated, with dark patches and erratic patterning.
The Rock Hind Grouper has a huge head and a prominent lower jaw. Its brow slopes slightly, and its form is concave. The pupils are round and black despite the small size of the eyes. Large and equipped with pointed teeth, the mouth is made for grabbing and consuming prey. An operculum, a rigid bony plate, protects the gills.
Habitat and Distribution
The Rock Hind Grouper is a fish that lives near reefs and prefers the ledges and rocks in the western Atlantic Ocean. Its range includes the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, stretching from the eastern coast of the United States to Brazil. In addition to shallower waters close to rocky shorelines, the rock hind grouper can also be found in depths between 60 and 350 feet.
Behavior and Diet
The Rock Hind Grouper is a lonely fish that spends the daytime lurking in cracks and caves. It becomes more active at night and goes hunting for prey. Cephalopods, tiny fish, and crabs make up most of its food. Due to its opportunistic feeding style, it will consume any accessible prey in its habitat.
Reproduction
The Rock Hind Grouper is a lonely fish that spends the daytime lurking in cracks and caves. It becomes more active at night and goes hunting for prey. Cephalopods, tiny fish, and crabs make up most of its food. Due to its opportunistic feeding style, it will consume any accessible prey in its habitat.
Conservation Status
The Rock Hind Grouper is a parthenogenetic hermaphrodite, which means it is born female and later transforms into a male. The transformation occurs when the fish attains a particular shape and age, usually between the ages of 5 and 7. The Rock Hind Grouper, as a female, lays eggs, which are fertilized by a male during spawning. Ocean currents sweep away the larvae after the eggs hatch.
Fishing Regulations
Although the rock hind grouper is popular among recreational anglers, it is also commercially fished for its meat. The National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) and the Gulf of Mexico Fishery Management Council (GMFMC) set fishing regulations for the rock hind grouper in the United States.
Recreational anglers can catch one rock hind grouper per person per day in the Gulf of Mexico and one in the Atlantic Ocean, with a minimum size limit of 16 inches in the Gulf of Mexico and 20 inches in the Atlantic Ocean. Annual catch limits and quota restrictions apply to commercial fishing for rock hind grouper.
Fisheries Management
The Rock Hind Grouper fishery is managed collaboratively by the National Marine Fisheries Service and the Gulf of Mexico Fishery Management Council. They employ various management strategies, such as catch limits and size limits.
What are the Rock Hind Grouper Fishing Regulations and Limits in Florida?
The Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) establishes rock fishing regulations in Florida. These rules are in place to protect the species while also ensuring its long-term use by recreational anglers and commercial fishermen.
Recreational Fishing Regulations
In Florida, recreational anglers can catch one rock hind grouper per day, with a size limit of 16 inches in total length. This applies to all state and federal bodies of water off Florida’s coast.
It is also essential to remember that when fishing for Rock Hind Grouper, only hook-and-line gear is permitted, and the use of spears, gigs, or other methods is prohibited. There are seasonal closures for the recreational harvest of Rock Hind Grouper in addition to the bag and size limit.
The recreational harvest of rock hind grouper in Atlantic waters is prohibited from January 1st to April 30th of each year. The recreational harvest of Rock Hind Grouper in the Gulf of Mexico waters is not permitted from February 1st to March 31st of each year.
Commercial Fishing Regulations
The Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission regulates commercial fishing for Rock Hind Grouper. Commercial fishermen are subject to quotas and other restrictions to ensure the sustainability of the fish.
Commercial fishermen in Florida can catch Rock Hind Grouper using hook-and-line or vertical line gear. The use of spearfishing gear or other methods, on the other hand, is prohibited.
Commercial Rock Hind Grouper have a minimum size limit of 12 inches, and fishermen must have a valid federal reef fish permit and a Florida saltwater fishing license. To avoid overfishing, commercial fishermen must adhere to specific catch limits and quantitative restrictions for Rock Hind Grouper in Florida waters.
To ensure that these provisions effectively maintain healthy populations of Rock Hind Grouper and other reef fish species, the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission works collaboratively with federal agencies such as the National Marine Fisheries Service.
Enforcement of Regulations
The Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission enforces Rock Hind Grouper fishing regulations through education, outreach, and law enforcement. Officers from the FWC patrol state and federal waters to ensure that anglers and commercial fishermen abide by the rules and regulations.
Financial penalties, seizure of fishing gear, and even prison sentences are possible penalties for violating Rock Hind Grouper fishing regulations in Florida. Anglers and commercial fishermen should become acquainted with the current laws and ensure that they are followed to avoid penalties and contribute to the conservation of the species for subsequent generations.
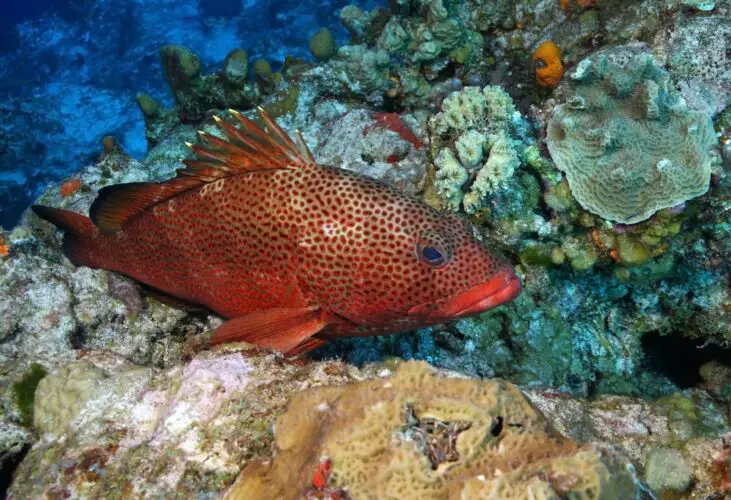

What are some sustainable fishing practices for Rock Hind Grouper?
What are some sustainable fishing practices for Rock Hind Grouper? To ensure the survival of Rock Hind Grouper and the overall health of the ecosystem, sustainable fishing practices are required. Here are some sustainable Rock Hind Grouper fishing techniques.:
Regulations and Restrictions
Regulations and restrictions on fishing are essential to safeguarding Rock Hind Grouper populations. This involves fishing seasons, catch limits and minimum size limits. Such laws ensure that the Rock Hind Grouper population does not decline to dangerously low levels and that the species can replenish itself over time.
Alternative fishing methods
Alternative fishing methods, such as hook and line, spearfishing, and trap fishing, can be more sustainable and decrease bycatch, especially in comparison to trawling or gillnetting. These methods can also be more selective, focusing on a specific species while leaving other fish alone. Additionally, biodegradable fishing gear can prevent ghost fishing, which occurs when lost equipment continues to trap and kill fish.
Aquaculture
Aquaculture or fish farming is another method for ensuring a sustainable supply of rock hind grouper. Farmed Rock Hind Grouper may serve as a different source of fish while reducing pressure on wild populations. Aquaculture can also ensure that the fish are raised in confined areas with less exposure to disease and parasites and make better use of resources like water and feed.
What are the major threats facing Rock Hind Grouper?
What are the major threats facing Rock Hind Grouper? Fundamentally, the Rock Hind Grouper, like many other marine species, is faced with several risks to the sustainability of its population. The following are some of the main threats this species faces:
Habitat Destruction
As with many marine species, the Rock Hind Grouper is seriously threatened by habitat degradation. The habitats on the seafloor that the Rock Hind Grouper depends on for food and shelter can be destroyed by human activities like coastal development, dredging, and bottom trawling.
Overfishing
Rock hind grouper are seriously threatened by overfishing, especially in regions targeted for commercial and recreational fishing. Overfishing of the rock hind grouper can have detrimental effects on both the species’ population and the ecosystem as a whole.
Since Rock Hind Grouper are the top predators in the food chain, their extinction could have a ripple effect on the environment, leading to both an increase in prey populations and a fall in predator populations.
Climate Change
Another major threat to the Rock Hind Grouper is climate change. The habitat and food supplies of fish can be significantly impacted by increasing marine temperatures, ocean acidification, and ocean current changes. These changes may affect the fish’s capacity to locate food, reproduce, and survive.
Bycatch
Like many other fish species, rock hind grouper can unintentionally get entangled in fishing equipment like nets, lines, and traps. This is referred to as “bycatch,” and commercial fishing operations all over the globe struggle with it severely.
Bycatch may damage the general health and sustainability of fish populations by causing the death of non-target species like rock hind grouper. Bycatch levels can occasionally be so high that they endanger the viability of particular species.
Pollution
Pollution from agricultural and industrial waste can hurt the habitat’s water quality. This contamination may affect the fish’s health and, in extreme instances, result in death.
What are the Roles of Rock Hind Grouper in the Ecosystem and Food Chain?
What are the Roles of Rock Hind Grouper in the Ecosystem and Food Chain? They are crucial in the western Atlantic Ocean’s ecosystem and food chain. It consumes smaller fish, crustaceans, and mollusks as predatory fish, acting as an essential regulator of their populations.
Predatory behavior
The Rock Hind Grouper is an opportunistic predator, which means it will eat a variety of prey species according to availability and size. It feeds on fish like snappers, grunts, small groupers, crustaceans like lobsters and crabs, and mollusks like clams and squid.
Preyed upon by other species
Larger predators, such as sharks and barracudas, feed on rock hind grouper. These predators may prey on rock hind grouper because of its quantity and size or be omnivorous. Other predatory fish could prey on the Rock Hind Grouper throughout its juvenile phases when it is smaller and more vulnerable.
Human consumption
Rock Hind Grouper is an essential food source for humans in addition to its position in the food chain, particularly in offshore communities where fishing is a significant industry. Its high protein content and mild flavor make it a favorite culinary ingredient.
Overfishing and incidental bycatch, on the other hand, can hurt the Rock Hind Grouper population as well as the overall health of the habitat. As a result, it is critical to adopt sustainable fishing practices and regulations to guarantee the species’ existence and the balance of the ecosystem in which it lives.
Conclusion
The Rock Hind Grouper is a species of fish that lives in the western Atlantic Ocean, specifically the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. It is a grouper species that can grow up to 30 inches long and is known for its distinctive coloring and delicious flavor.
Whereas the Rock Hind Grouper is a popular commercial and recreational target, it is also susceptible to overfishing and unintentional bycatch, which can harm its population and the overall health of our oceans. To ensure that the Rock Hind Grouper and other sea creatures continue to thrive for future generations, it is essential to adopt sustainable fishing practices and regulations.










Pingback: What is a Blacktip Grouper? | Reel Fishing Guru